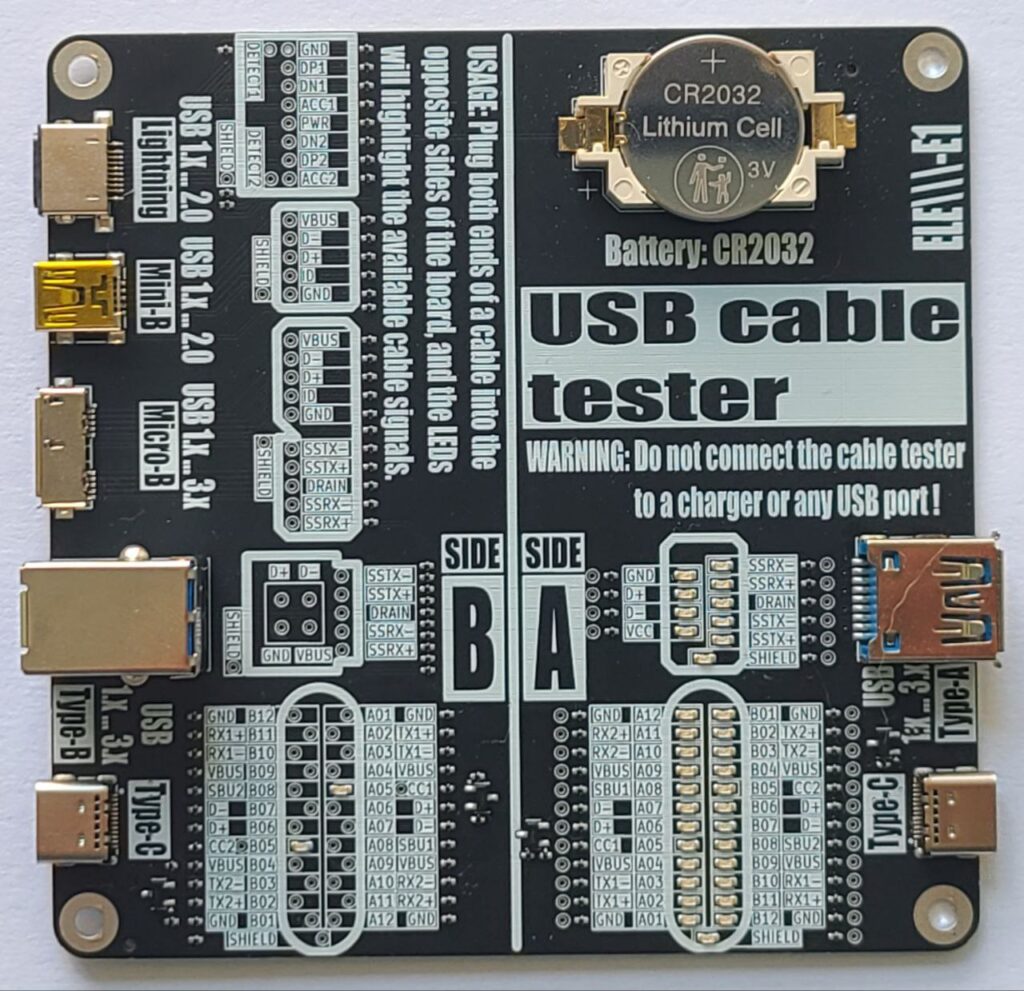
Introduction The USB Cable Tester is a diagnostic tool designed to verify internal wiring of various USB cables with minimum length of 12 inches or 30 centimeters. This manual provides instructions for use of the tester. Overview Power Source: CR2032 Lithium Cell (3V). Purpose: Test pin continuity and identify passive USB cables. Connector combinations supported:…
Author Archives: Elerain
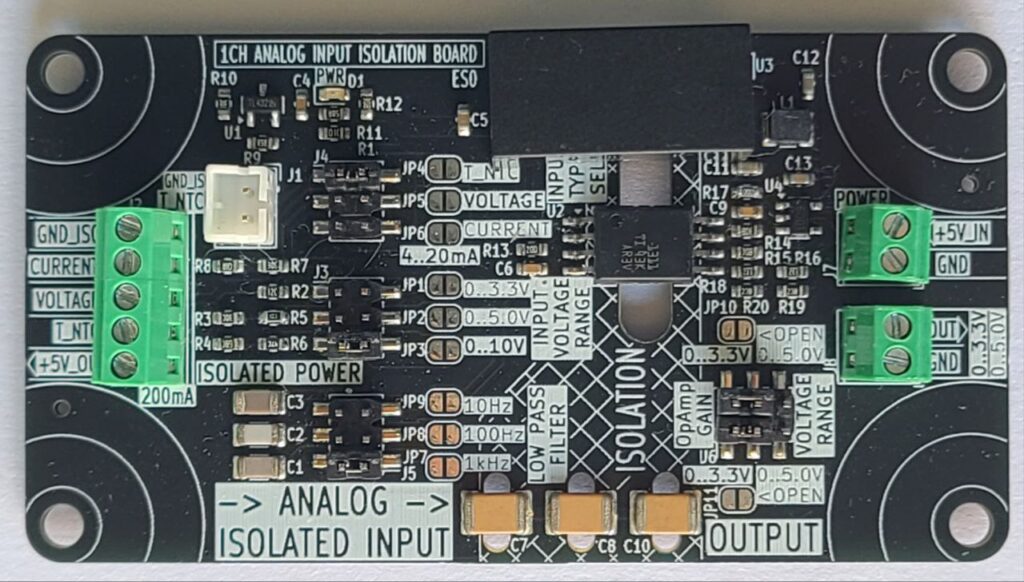
Specification & User Manual Product Name: 1CH 5kV Analog Isolator Board Model: 1CH-A-ISO 1. General Description The 1CH 5kV Analog Isolator Board is designed to provide safe galvanic isolation between field analog signals and microcontroller systems. It supports temperature sensing, current loop interface (4–20mA), and voltage input signals (0–3.3V, 0–5V, 0–10V). The board delivers a…
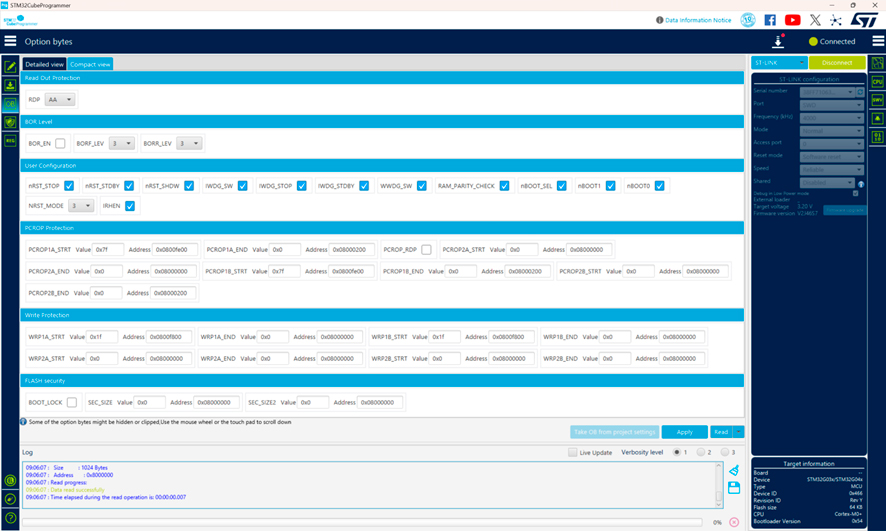
When you create a new STM32G0 project in STM32CubeIDE, the debugger initially seems to work correctly. Code execution runs normally until the first interrupt occurs (in my case, the SysTick interrupt). At that moment the program counter suddenly jumps outside of the Flash memory space, so the debugger can no longer show valid source code corresponding to the PC value. At first…
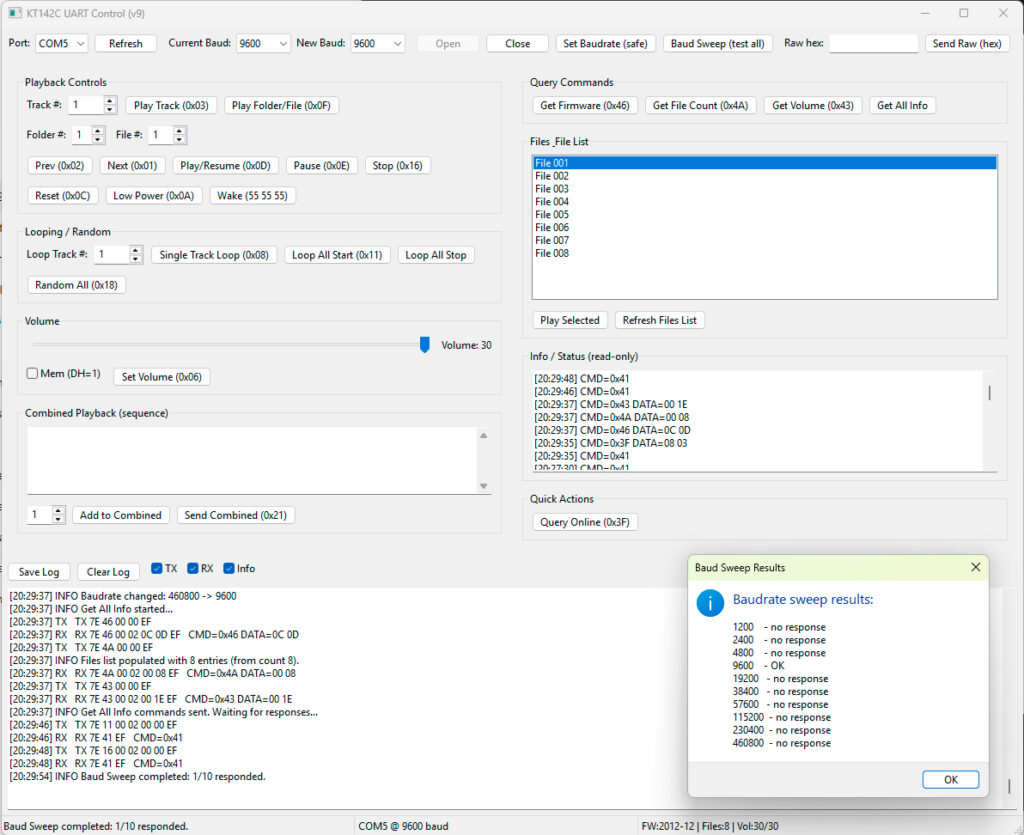
Introduction The KT142C UART Control GUI (v9) is a comprehensive Python-based interface designed to control the KT142C audio module via UART. This GUI enables both manual operations and automated test sequences, offering a user-friendly yet powerful tool for audio playback, and device configuration. Built with wxPython for the graphical user interface and pySerial for serial…
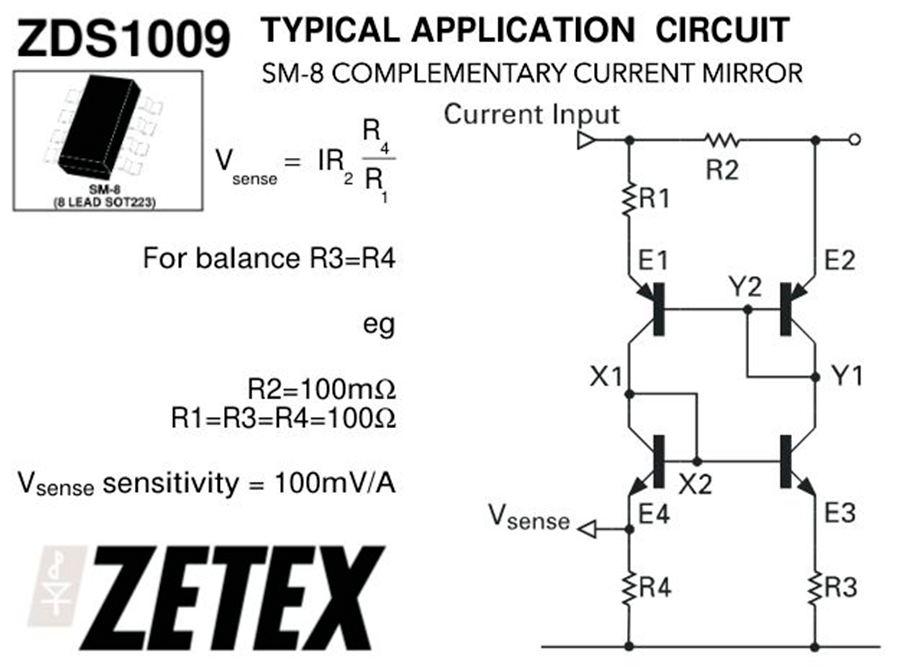
High-Side Current Sensing Using Dual Current Mirrors — ZDS1009 Example The ZDS1009 datasheet includes an interesting high-side current sensing schematic that uses two matched current mirrors to translate the voltage drop across a shunt resistor into a ground-referenced output current. This implementation demonstrates an efficient analog method for high-side current measurement using only discrete transistors…
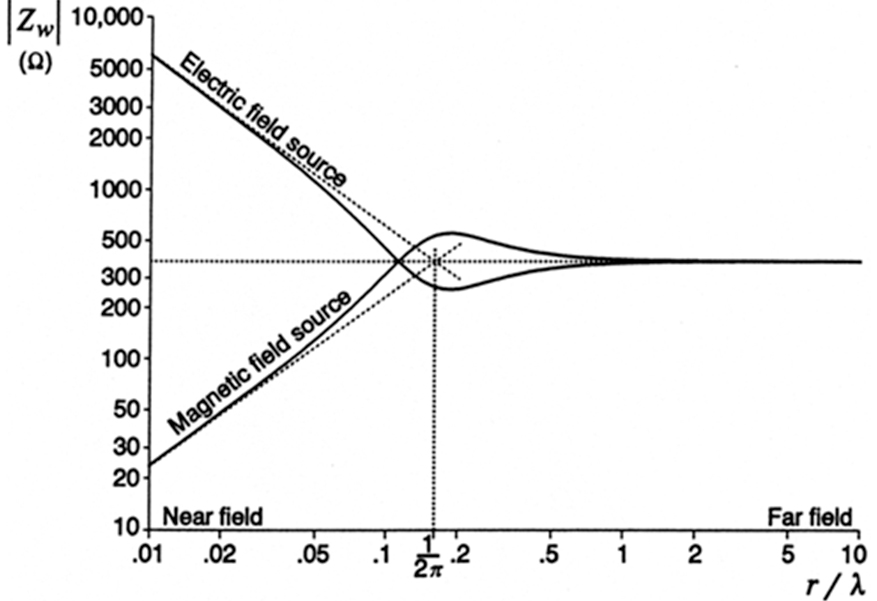
Conducted and Radiated EMI – Practical Troubleshooting Guide Understanding EMC, EMI, and EMS EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) The overall discipline ensuring that electronic devices and systems function properly in their electromagnetic environment without causing or suffering from interference. EMC = the ability to coexist with other electronics. EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) Any unwanted electromagnetic disturbance generated by…
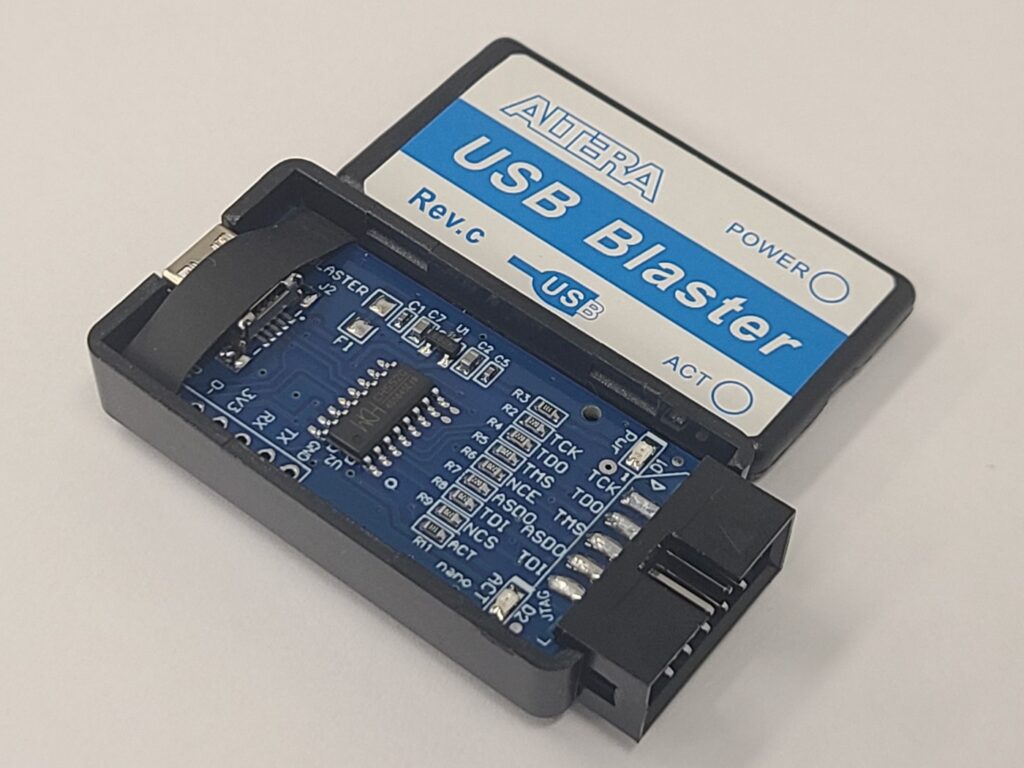
Chinese engineers have developed a low-cost USB-Blaster equivalent tool based on CH552G microcontroller to work with INTEL (ALTERA) CPLD/FPGA. The problem is that the preloaded firmware doesn’t work reliably. CH552G is an 8-bit 8051 MCU that has a fair number of features for the price (<1$). Doug Brown posted a practical step-by-step guide for reflashing…
A simple, powerful method for finding weak points in your electronics Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is one of the most destructive and unpredictable threats in electronic systems. Even a tiny spark can corrupt data, reset a microcontroller, or permanently damage sensitive components. Professional ESD guns cost hundreds to thousands of dollars — but there is a…
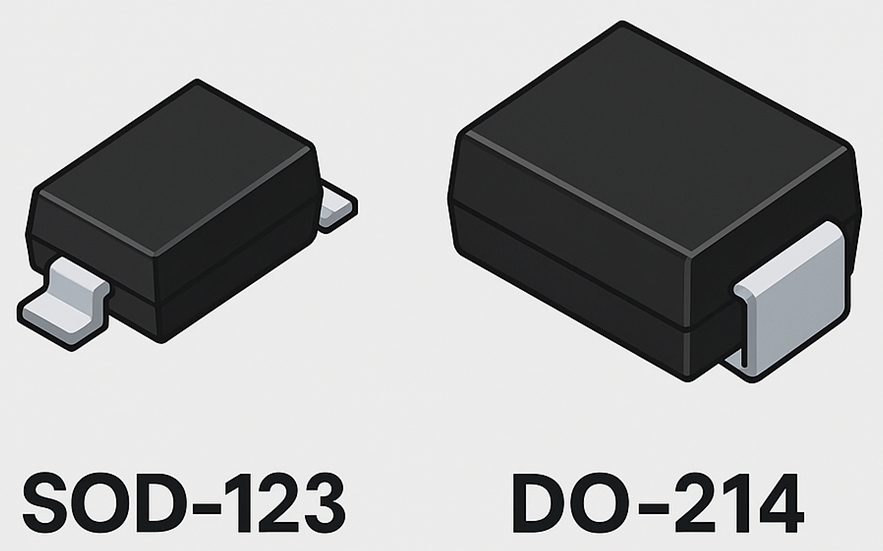
Choosing the right diode is critical for optimizing efficiency, thermal performance, and switching behavior in modern power electronics. Two of the most common families—Schottky diodes and ultrafast recovery diodes—are often used in similar circuits, but their electrical characteristics make them ideal for very different applications. This article provides a clear engineering explanation of both types,…
How to safely interface 3.3 V and 5 V logic without specialized ICs In embedded systems, it is extremely common to connect devices that operate at different logic voltages. Many modern microcontrollers run at 3.3 V, while older devices, sensors, serial peripherals, and some modules still use 5 V logic. Although dedicated level-shifter ICs exist,…
- 1
- 2